Difference between Session and Cookies
When building a website, we need to remember user information whether it's login details, preferences or shopping cart items. Two common ways to store this data are sessions and cookies.
- Cookies are small pieces of data stored in the user's browser. They help remember things like login status or preferences even after closing the website.
- Sessions store user data on the server, making them more secure and ideal for storing temporary or sensitive information.
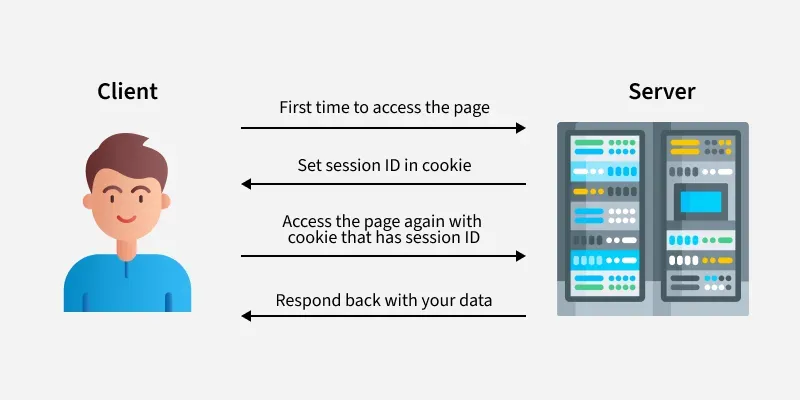
Difference
| Feature | Cookies | Sessions |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Location | Stored on the client side (browser). | Stored on the server side. |
| Data Security | Less secure, as it is exposed to the client. | More secure, as data is stored on the server. |
| Performance | Faster as data is stored on the client. | Slightly slower as each request requires server processing. |
| Data Size Limit | Limited to 4KB per cookie. | Can store large amounts of data. |
| Expiration | Can be set manually (maxAge, expires). | Expires automatically after inactivity or when explicitly destroyed. |
| Data Persistence | Persists even after the browser is closed (unless expired). | Data is lost once the session expires or the server restarts (unless stored in a database). |
| Used for Authentication | Often used for storing authentication tokens like JWT. | Commonly used for session-based authentication. |
| Example | Google, Facebook, Amazon, YouTube, Netflix etc. | Banking Websites, E-learning Platforms, Government Portals, Job Portals etc. |
- Cookies: Used for remembering login states and tracking users across multiple sessions.
- Sessions: Used for temporary and secure storage during a single login session.